

Hereditary or spontaneous mutations ( > 45 genes are known as triggers e.g., mutations in the rhodopsin gene ).
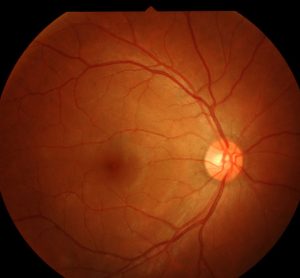
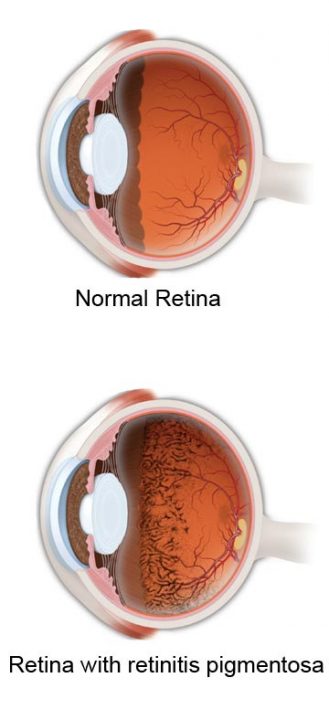
Epidemiology: early onset ( 5–30 years).Definition: progressive hereditary dystrophy of the retina or of the photoreceptors and the retinal pigment epithelium.Treatment: vitrectomy with removal of epiretinal membranes and the internal limiting membrane of the retina.Secondary (e.g., to vitreous detachment, due to trauma, following laser therapy).Definition: central small break in the macula.Rarely: laser coagulation (in extramacular localization), photodynamic therapy.Ophthalmoscopy: roundish detachment of the central retina.Relative scotoma (perception of a gray area or shadow in the central field of vision).Patients perceive images as smaller than they are.Glucocorticoids and an increase in the diastolic blood pressure are possible risk factors.Pathophysiology: defect in the area of Bruch's membrane/ pigment epithelium → fluid leakage from the sclera into the subretinal space → serous retinal detachment.Definition: serous retinal detachment at the posterior pole of the eyeball (at the macula or in the perimacular region) due to a defect in the pigment epithelium.Anomaloscope: instrument used to diagnose quantitative and qualitative defects in color perceptionĬentral serous retinopathy (central serous chorioretinopathy).Ishihara color test: set of color-dotted plates used to diagnose deuteranopia and protanopia.Clinical features: difficulties distinguishing colors from one another.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
